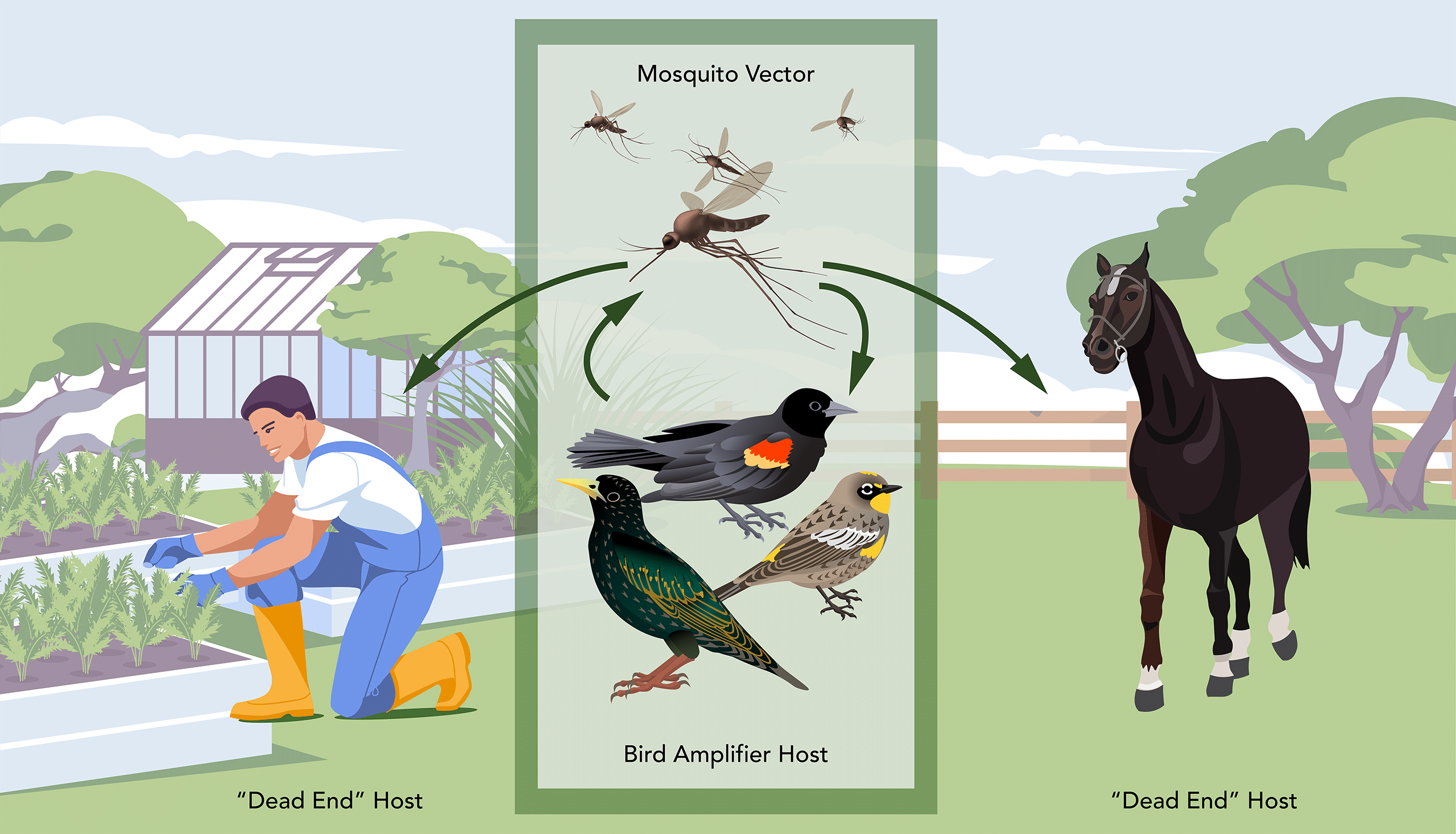
West Nile Virus Transmission Cycle
West Nile virus (WNV) is the leading cause of mosquito-borne disease in the continental United States. West Nile virus is mainly spread to humans, horses, and birds through the bite of an infected mosquito that become infected when they feed on infected birds, which often carry the disease. However, there have been a very small number of cases where the virus was spread by blood transfusion, organ donation, or from mother to baby during pregnancy, birth, or when breastfeeding. Cases of WNV occur during mosquito season, which starts in the summer and continues through fall. There are no vaccines to prevent or medications to treat WNV in people. Fortunately, most people infected with WNV do not feel sick. For people who do feel sick, symptoms can include fever, headache, tiredness, nausea, vomiting, muscle aches, and a rash. Symptoms usually last from a few days to a few weeks.
You can reduce your risk of WNV by using insect repellent, draining any standing water around your yard, and wearing long-sleeved shirts and long pants to prevent mosquito bites.